Example Searches:
CVE
Threat Actors
Countries
Vendors
Severity
Known Exploited

|
Description: [AI generated] Founded in 1868, sfhumanesociety.org is associated with the San Francisco Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (SFSPCA). As one of the world's pioneer animal welfare organizations, its mission is to save and protect animals, provide care and treatment, advocate for their welfare, and enhance the human-animal bond. It offers services including animal adoption, veterinary care, and community education.
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|

|
Description: [AI generated] The Meeks Group is an Oklahoma-based company that specializes in providing various advertising services to businesses. Their service range includes graphic design, digital printing, exterior and interior signage, promotional items, and direct mail marketing. They aim to aid businesses in enhancing their brand visibility and reaching their target audience effectively.
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|

|
Description: CWE ID: CWE-532 (Insertion of Sensitive Information into Log File)
CVSS: 7.5 (High)
Vector: CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:N/A:N
Affected Component: Para Server Initialization Logging
Version: Para v1.50.6
File Path: para-1.50.6/para-server/src/main/java/com/erudika/para/server/utils/HealthUtils.java
Vulnerable Line(s): Line 132 (via logger.info(...) with root credentials)
Technical Details:
The vulnerability is located in the HealthUtils.java file, where a failed configuration file write triggers the following logging statement:
logger.info("Initialized root app with access key '{}' and secret '{}', but could not write these to {}.",
rootAppCredentials.get("accessKey"),
rootAppCredentials.get("secretKey"),
confFile);
This exposes both access and secret keys in logs without redaction. These credentials are later reused in variable assignments for persistence but do not require logging for debugging or system health purposes.
References
https://github.com/Erudika/para/security/advisories/GHSA-v75g-77vf-6jjq
https://github.com/Erudika/para/commit/1e8a89558542854bb0683ab234c4429ad93b0835
https://github.com/advisories/GHSA-v75g-77vf-6jjq
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|
|
CVE-2024-22569 |
Description: Stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerability in POSCMS v4.6.2, allows attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted payload to /index.php?c=install&m=index&step=2&is_install_db=0.
EPSS Score: 0.11% SSVC Exploitation: none
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|

|
🚨 Marked as known exploited on May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago).
Description: Two critical vulnerabilities affecting the open-source forum software vBulletin have been discovered, with one confirmed to be actively exploited in the wild. [...]
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|

|
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|

|
Description: The US Treasury said cryptocurrency investment schemes like the ones facilitated by Funnull Technology Inc. have cost Americans billions of dollars annually.
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|

|
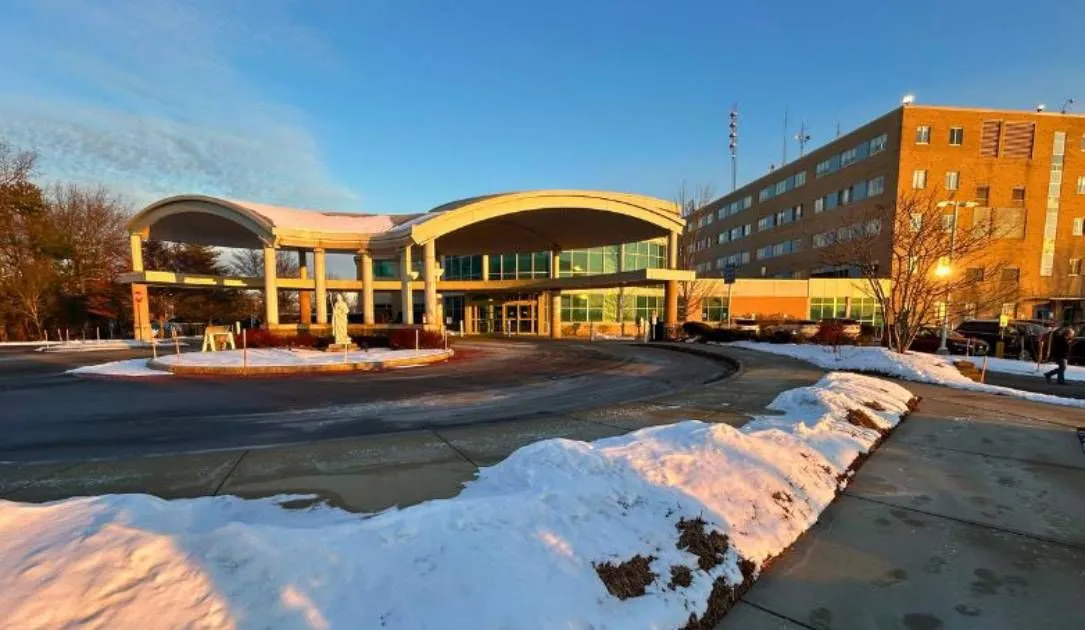
Description: Three hospitals run by Catholic healthcare organization Covenant Health are dealing with a cyberattack that forced the facilities to shut off all access to data systems.
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|
|
Description: Microsoft announced today that the Windows 11 Notepad application is getting a text formatting feature supporting Markdown-style input. [...]
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|

|
May 30th, 2025 (10 days ago)
|
